某型渣土车轻量化U型车厢结构设计(含CAD图,CATIA三维图,有限元分析)
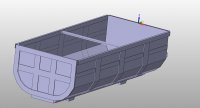
某型渣土车轻量化U型车厢结构设计(含CAD图,CATIA三维图,有限元分析)(任务书,开题报告,文献摘要,外文翻译,论文说明书18000字,CAD图10张,CATIA三维图,有限元分析)
摘要
本文针对某型渣土车车厢,基于材料和结构,提出了轻量化车厢结构优化方案。在材料方面采用NM450、Q690D高强度钢替代传统的Q345钢板,降低对标矩形车厢各总成的厚度;结构方面由原矩形车厢结构更换为U形车厢结构,借助建模和分析软件使其在符合刚度、强度要求下达到质量最轻。目标在车厢承载能力不变的情况下,车厢相对于对标矩形车厢减重。所得成果在节能减排方面具有重要意义。
论文主要研究了:
1.高强度钢与传统钢材之间的等强度厚度替换关系。
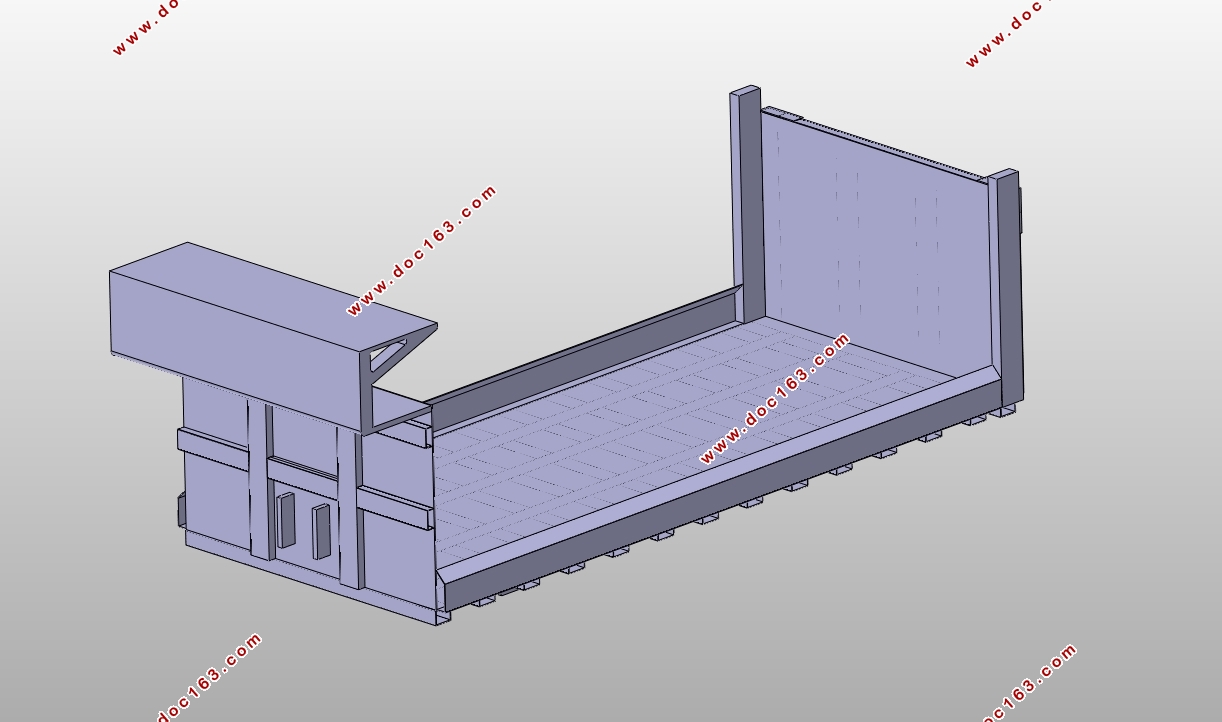
2.对标矩形车厢和高强度钢U型车厢的结构设计与建模。
3.对标矩形车厢与高强度钢U型车厢各工况下有限元分析。
4.优化设计后产生的节能减排效益。
研究结果表明:
通过优化对标矩形车厢的结构与材料可大量降低加强筋的使用数量和板材厚度,车厢总质量降低约33%。
更换高强度钢导致车厢下降的刚度可以通过U型结构补偿。
轻量化后的U型车厢重心高度有所增加,但在安全标准以内。 [资料来源:http://www.doc163.com]
轻量化后的U型车厢相对于对标矩形车厢容积基本不变,均约为17m³。
5. 轻量化后的U型车厢相对于对标矩形车厢,应力应变大小情况基本一致,部分区域U型车厢偏大但不影响使用。在应力应变均匀分布情况上,U型车厢相对于对标矩形车厢甚至更优。
6. 对标矩形车厢总变形量设置过小,作为渣土车车厢性价比较低,轻量化后的U型车厢平均总变形量约为4mm,在承载性能基本不变的情况下性价比更高。
本文特色:1.采用NM450、Q690D高强度钢等强度替代传统Q345钢,保证钢材厚度利用的最大化。2.车厢采用U型结构,保证装载能力基本不变的前提下提高了车厢的刚度强度。3.分析对比了对标矩形车厢与本文优化设计车厢在质量、承载力、刚度强度、应力应变、节能减排效益等综合性能上的差异。
关键词:渣土车车厢、轻量化、结构优化设计、等强度厚度替换、高强度钢、U型车厢
Abstract
This paper puts forward the structure optimization scheme, which aims atone type of theslag carcarriages, and the structure optimization scheme is based on the materials and structure. In terms of the materials, replace the traditional Q345 steel by theNM450、Q690D high strength steel, which reduce the thickness of each assembly of the traditional slag car carriages. In terms of the structure, In accordance with the Stiffness and strength requirements, we use the modeling and the analysis software to replace the traditional rectangular carriagesby the U-type carriages, and reduce the carriages weight. The goal is that in the case of the same carrying capacity of the carriages, the carriages weight should be reduced. The results are of great significance in energy conservation and emission reduction.
The paper mainly studies that:
Equal strength thickness replacement relationship between high strength steel and traditional steel.
The Structural design and modeling between rectangular carriages and U-type carriages.
Finite element analysis of standard rectangular car and high strength steel U carriage under different working conditions
Efficiency of energy saving and emission reduction after optimization design
The result of research shows that
by optimizing the structure and material of the rectangular compartments, the number of stiffeners and the thickness of plates can be greatly reduced, and the total quality of the carriage will be reduced by about 33%.
replacement of high strength steel leads to a reduction in stiffness of the carriage, which can be compensated by the U structure.
The center of gravity of the lightweight u-type carriage has increased, but it is still within the safety standard.
[资料来源:http://Doc163.com]
The weight of the lightweight Ucarriage is basically unchanged from that of the standard rectangular car, which is about 17 cubic meters.
After the lighting weight, the u-shaped carriage is basically the same as that of the standard rectangular carriages, and the u-shaped carriages in some regions is large but not affected.In the case of the uniform distribution of stress and strain, the u-shaped carriages is even better than the rectangular one.
The total deformation of the standard rectangular compartment is too small. As the low cost of the car carriage, the average total deformation of the U carriage is about 4mm, and the performance price ratio is higher when the bearing capacity is basically unchanged.
The article characteristics:1.NM450、Q690D High strength steel is used to replace the traditional Q345 steel,and it ensures the maximum utilization of steel thickness.2. The carriages adopts u-type structure, whose stiffness isimproved, and also ensures the load capacity. 3. In terms of the comprehensive performance of the weight , bearing capacity, rigidity strength, stress strain and energy conservation and emission reduction, this paper analyzes and compares the differences between the traditional slag carriages and the optimal design carriages.
[版权所有:http://DOC163.com]
Key words:slag carcarriages; light weight; optimum structural design; Equal strength thickness replacement; high-strength steel; U-type carriages
本文研究的传统公路用渣土车属于自卸车的一种常规车型,其设计参数满足国家公路法规和汽车设计的规范要求。该车型按照国标(1589)要求四轴汽车最大允许总质量为35t,采用前顶式举升机构,车厢长度为5550mm中长车厢,前挡板底板厚8mm,后挡板底板厚8mm,承载底板厚10mm。具体参数如表2.1所示。
表2.1车型参数表
轴距(mm) 1550+4475+2315
整车外形尺寸(mm) 8640×2550×3491(长×宽×高)
车厢内尺寸(mm) 5400×2300×1435(长×宽×高)
最大承载质量(kg) 35000
最高车速(km/h) 78
载质量利用系数 1.00
轴距:1550代表前轴中心与车头前的距离,4475代表前轴中心与后轴中心的距离,2315代表后轴中心与车尾的距离。
[资料来源:Doc163.com]


目录
第1章绪论 1
1.1研究背景及意义 1
1.2轻量化分类 1
1.3国内外研究现状 2
1.3.1国内研究现状 2
1.3.2国外研究现状 2
1.4本文研究内容 3
第2章对标矩形车厢结构介绍及分析 4
2.1渣土车整车结构及参数 4
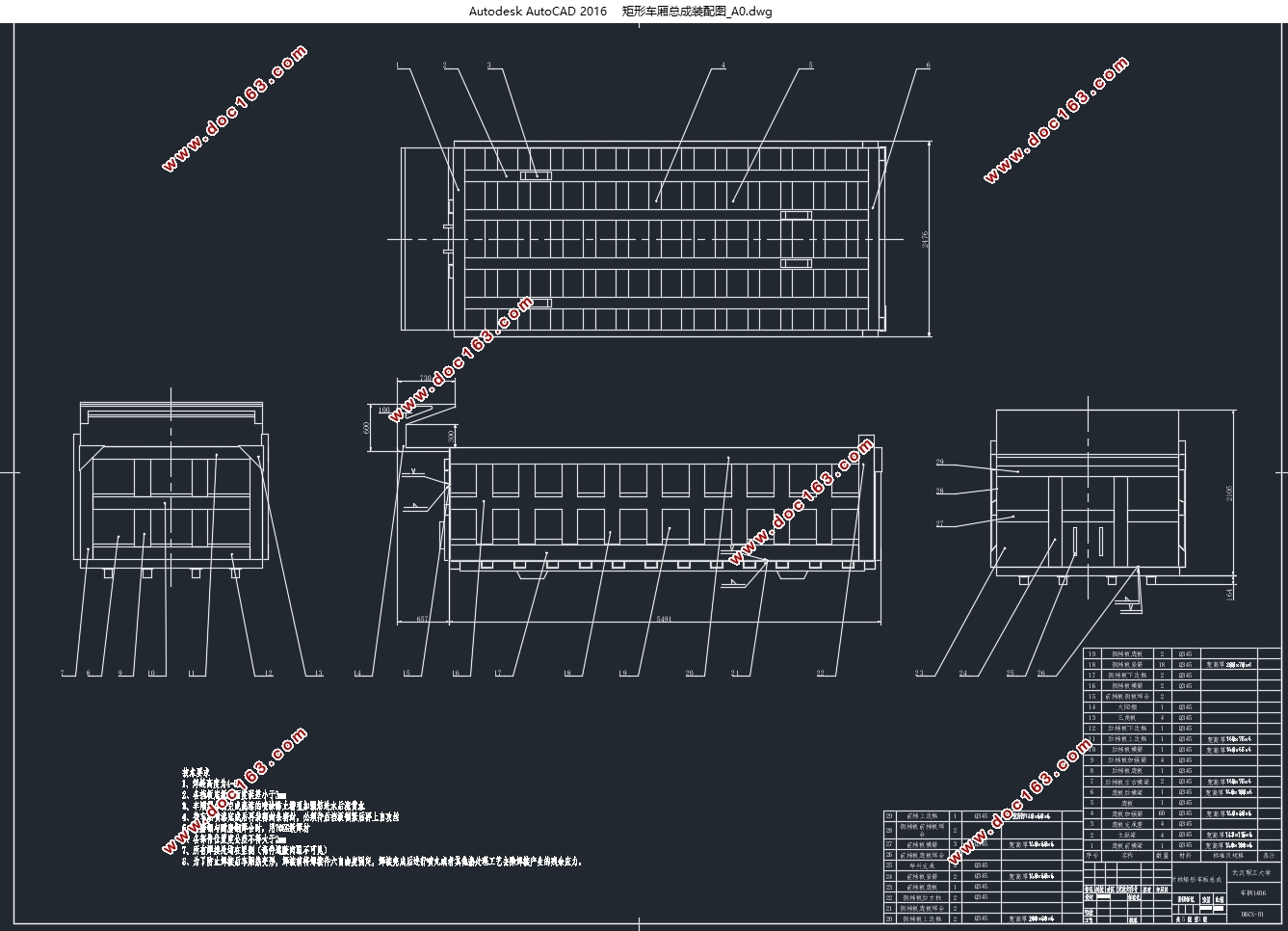
2.2对标矩形车厢的组成及特点 5
2.2.1对标矩形车厢前挡板总成及特点 5
2.2.2对标矩形车厢后挡板总成及特点 6
2.2.3对标矩形车厢侧挡板总成 7
2.2.4对标矩形车厢底板总成 8
第3章对标矩形车厢模型的建立 9
3.1对标矩形车厢建模的预处理和模型建立 9
3.3典型工况的选取和受力分析 11
3.3.1车厢整体的受力分析 11
3.3.2车厢各总成的受力分析 12
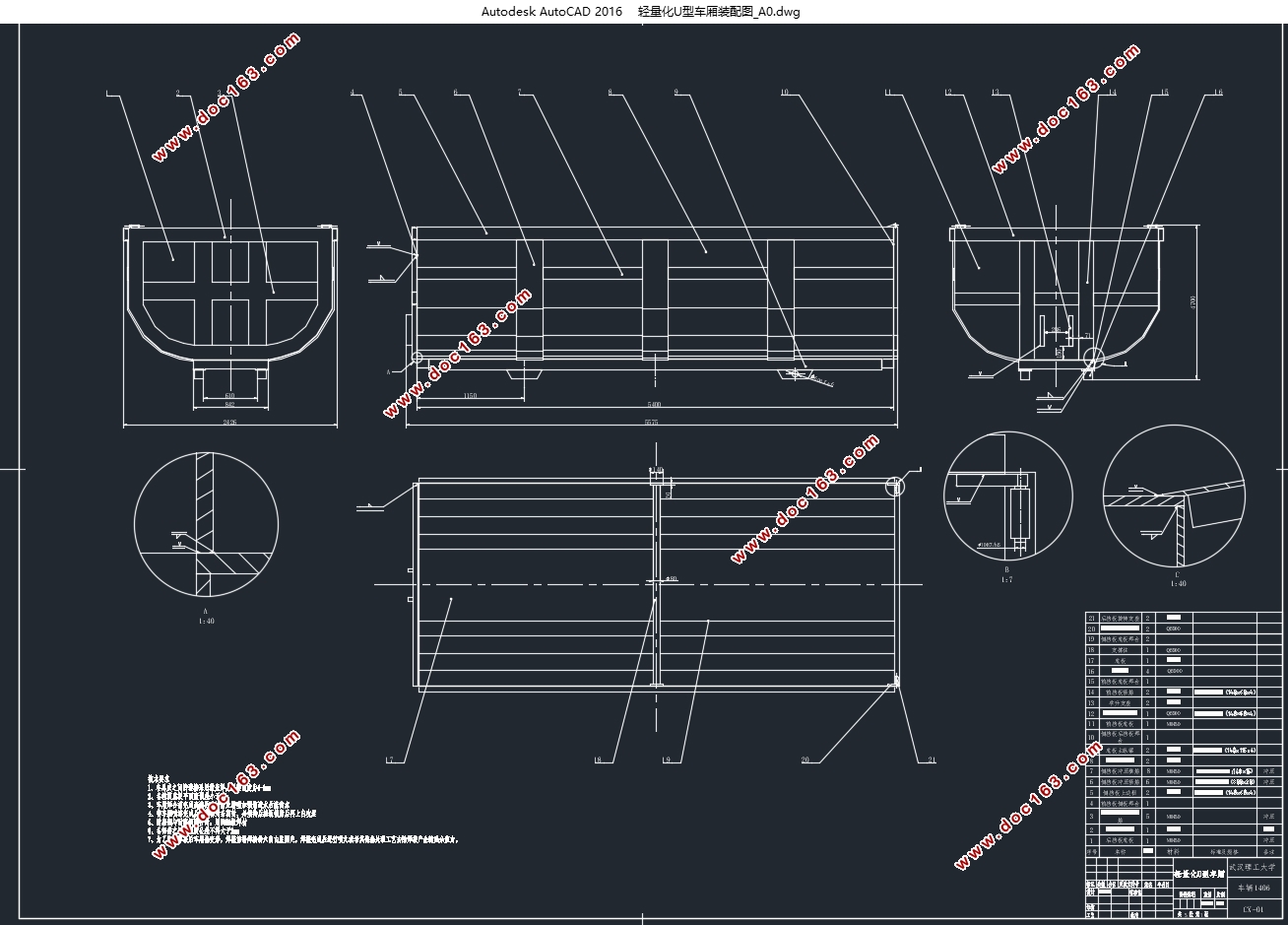
第4章 U型高强度钢车厢模型的建立 13 [资料来源:http://www.doc163.com]
4.1高强度钢板板厚等代设计计算公式的推导 13
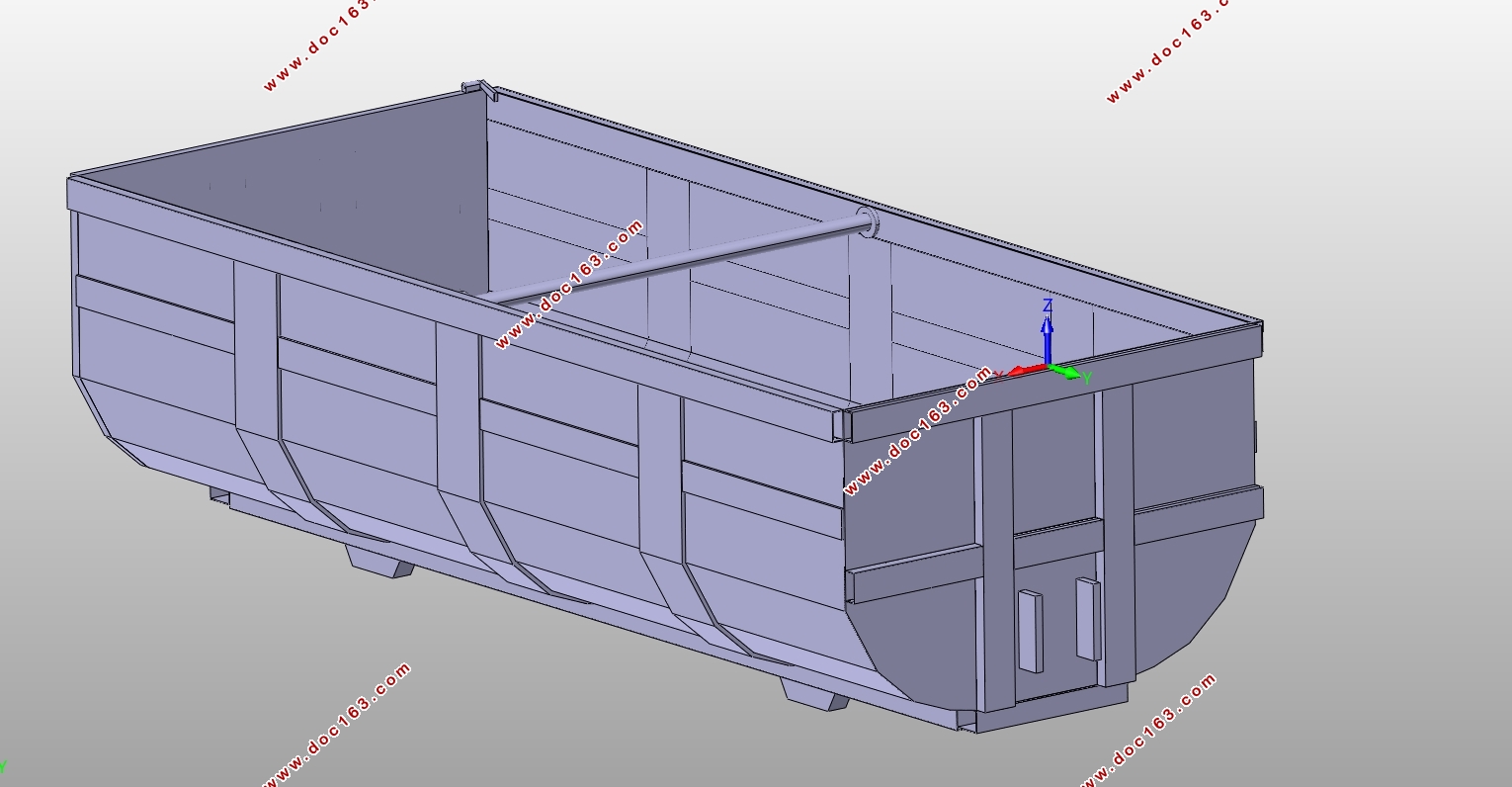
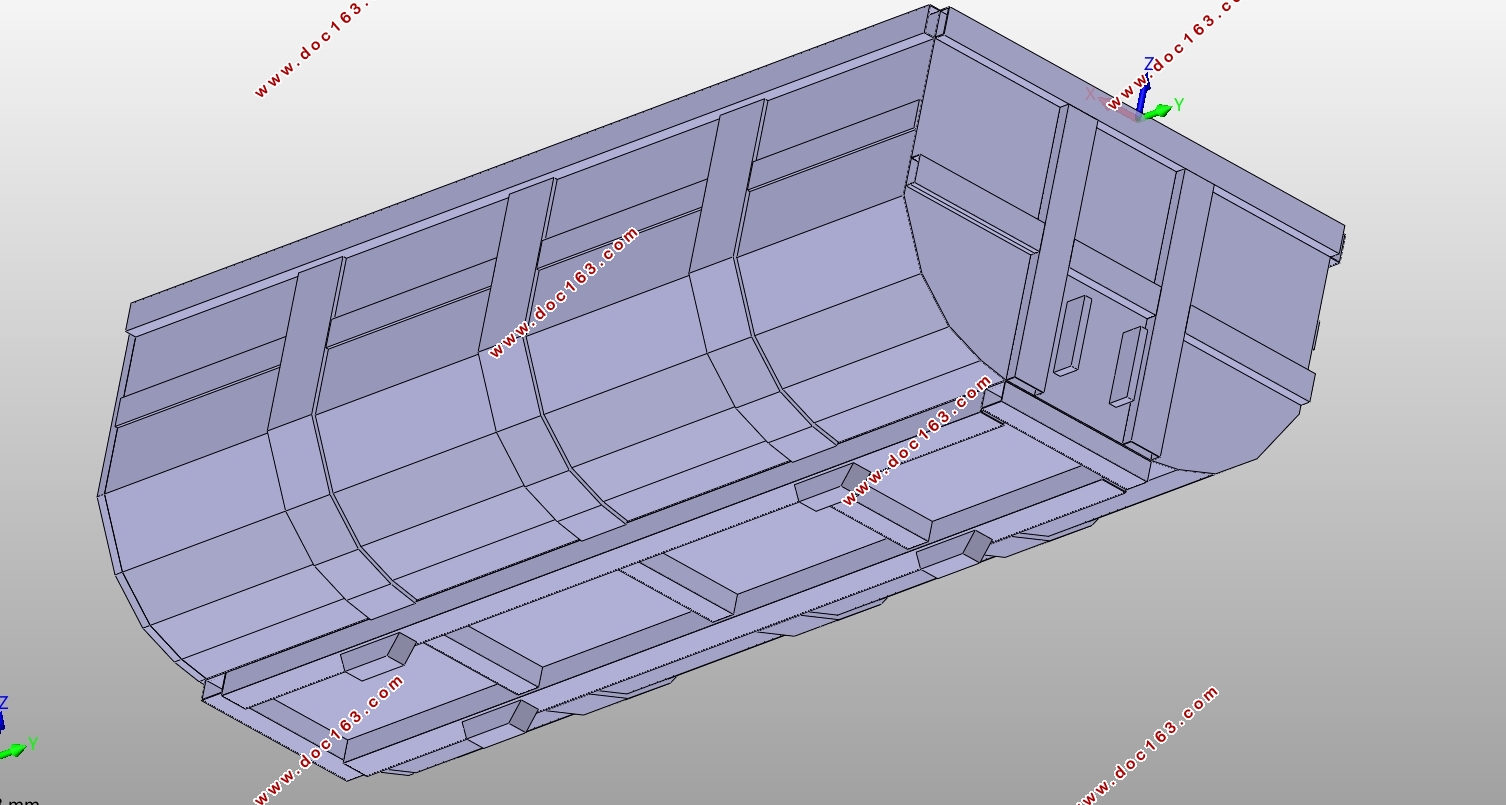
4.2 U型车厢各总成的设计 14
4.2.1车厢侧挡板总成的设计 14
4.2.2车厢底板总成的设计 15
4.2.3车厢前挡板总成的设计 16
4.2.4车厢后挡板总成的设计 17
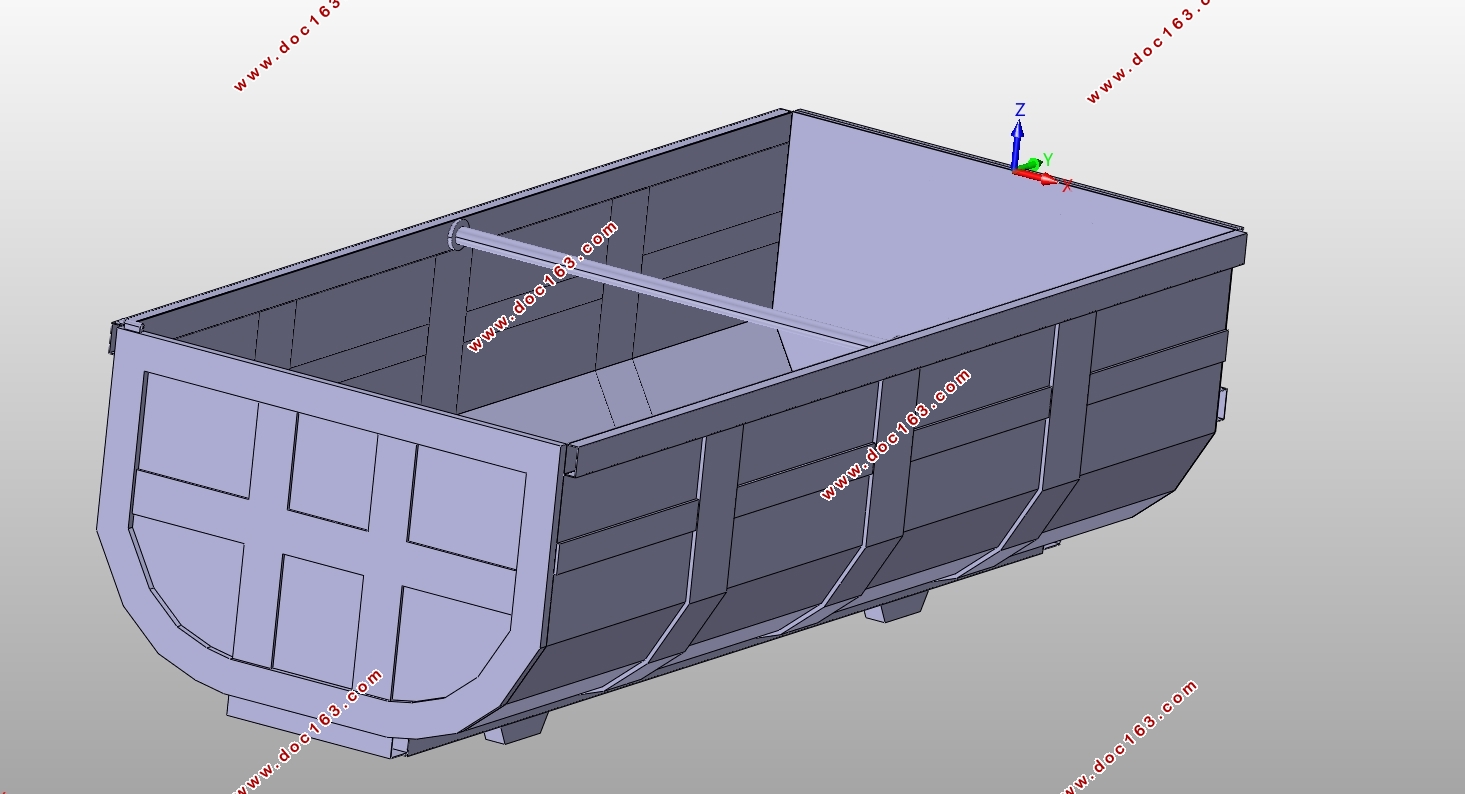
4.3建立U型高强度钢车厢模型 18
4.4U型车厢受力分析 19
4.4.1U型车厢整体的受力分析 19
4.4.2U型车厢各总成的受力分析 20
4.5对标矩形车厢与U型车厢模型的比较 21
第5章两种车厢的有限元分析 22
5.1车厢有限元分析前处理 22
5.1.1车厢模型的导入与划分网格 22
5.1.2车厢载荷的施加和约束条件 23
5.2车厢在满载工况下的有限元分析和比较 24
5.2.1车厢的总变形量比较 24
5.2.2车厢的应力比较 26
5.2.3车厢的应变比较 29
5.3车厢在满载举升瞬间的有限元分析和比较 31
5.3.1前挡板的总变形量比较 31
5.3.2前挡板的应力比较 32
5.3.3前挡板的应变比较 33
5.4两车厢总变形、应力应变对比总结 34
第6章.结论 35
参考文献 35
致谢 36
[来源:http://www.doc163.com]
下一篇:纯电动SUV总体设计与传动系参数匹配(含CAD零件图装配图)
