连杆工艺及扩孔夹具设计
连杆工艺及扩孔夹具设计(任务书,外文翻译,设计说明书13000字,cad图纸6张,工艺规程,答辩PPT)
摘要
连杆是柴油机中的主要传动件之一,它连接着活塞和曲轴,其作用是将活塞的往复运动转变为曲轴的旋转运动,并作用在活塞上的力传给曲轴以输出功率。连杆在工作中,除承受燃烧室燃气产生的压力外,还要承受纵向和横向的惯性力。因此,连杆在一个复杂的应力状态下工作。它既受交变的拉压应力、又受弯曲应力。连杆的主要损坏形式是疲劳断裂和过量变形。通常疲劳断裂的部位是在连杆上的三个高应力区域。连杆的工作条件要求连杆具有较高的强度和抗疲劳性能;又要求具有足够的钢性和韧性。连杆的尺寸精度、形状精度以及位置精度的要求都很高,而连杆的刚性比较差,容易产生变形,因此在安排工艺过程时,就需要把各主要表面的粗精加工工序分开。逐步减少加工余量、切削力及内应力的作用,并修正加工后的变形,就能最后达到零件的技术要求。本文主要论述了连杆的加工工艺及其夹具设计。
关键词: 连杆,变形,加工工艺,夹具设计
ABSTRACT
The connecting rod is one of the main driving medium of diesel engine, it is connected to the piston and the crankshaft, it’s role is to the reciprocating piston movement into rotary movement of the crankshaft, and the of the force in the piston to the crankshaft to the output power. When working, the connecting rod not only support the pressure from the gas chamber, but also bear the vertical and horizontal inertia force. Therefore the connecting rod works in a complex environment .The main damage of the connecting rod is fatigue and excessive deformation . The working conditions of the connecting rod require it has higher strength and fatigue performance, and has enough rigidity and toughness. The precision of size, the precision of profile and the precision of position , of the connecting rod is demanded highly , and the rigidity of the connecting rod is not enough, easy to deform, so arranging the craft course, need to separate the each main and superficial thick finish machining process. Reduce the function of processing the surplus , cutting force and internal stress progressively , revise the deformation after processing, can reach the specification requirement for the part finally . This text expounds mainly the machining technology and the design of clamping device of the connecting rod. [来源:http://Doc163.com]
Keyword: connecting rod ,deformation ,processing technology ,design of clamping device
1.本课题主要研究连杆的加工路线及扩孔夹具的设计;
2.在指导老师的指导下,能独立完成加工方案的拟定,编制工艺规程;
3.能熟练运用学过的理论知识,正确完成设计中的计算工作;
4.能熟练运用绘图软件绘制连杆及夹具图;
连杆的技术要求
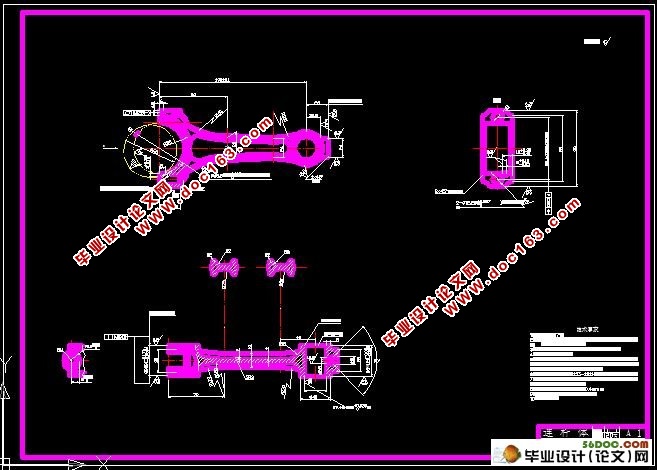
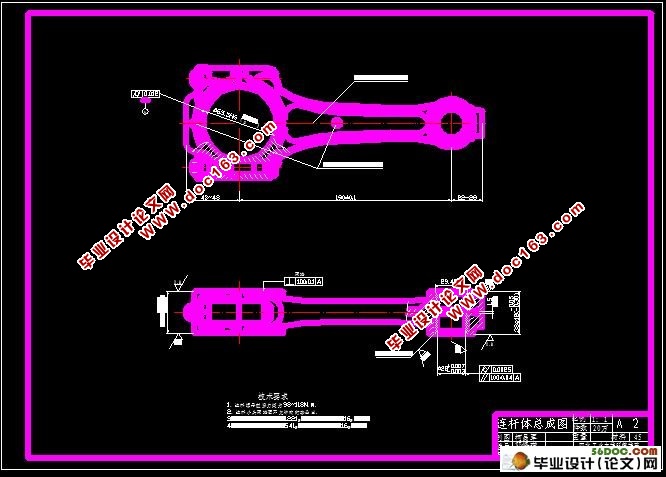
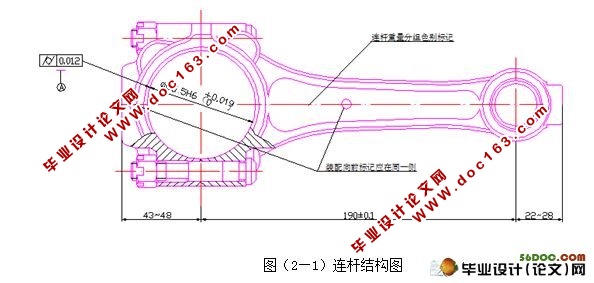
连杆上需进行机械加工的主要表面为:大、小头孔及其两端面,连杆体与连杆盖的结合面及连杆螺栓定位孔等。连杆的具体技术要求如下:
1 大、小头孔的尺寸精度、形状精度
为了使大头孔与轴瓦及曲轴、小头孔与活塞销能密切配合,减少冲击的不良影响和便于传热。大头孔公差等级为IT6,表面粗糙度Ra应不大于0.4μm;大头孔的圆柱度公差为0.012 mm,小头孔公差等级为IT8,表面粗糙度Ra应不大于3.2μm。小头压衬套的底孔的圆柱度公差为0.0025 mm,素线平行度公差为100:0.04mm。
2 大、小头孔中心距
大小头孔的中心距影响到发动机的效率,所以规定了比较高的要求:190±0.1mm。
3大、小头孔两端面粗糙度
连杆大、小头孔两端面间距离的基本尺寸相同,大小头两端面的尺寸公差等级为IT9,表面粗糙度Ra不大于0.8μm。 [版权所有:http://DOC163.com]
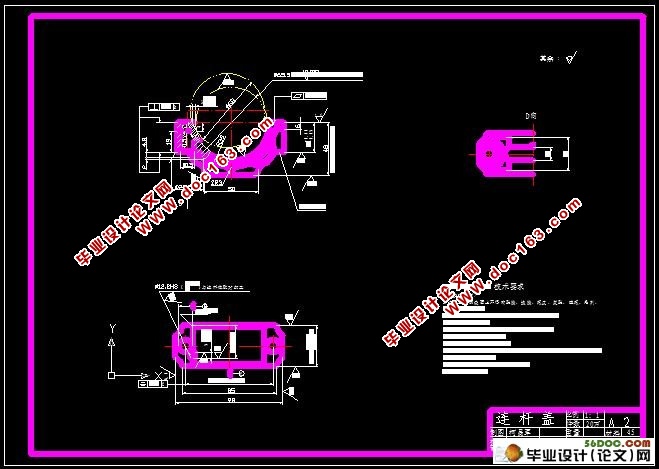
4 螺栓孔的技术要求
连杆在工作过程中受到急剧的动载荷的作用。这一动载荷又传递到连杆体和连杆盖的两个螺栓及螺母上。因此除了对螺栓及螺母要提出高的技术要求外,对于安装这两个动力螺栓孔及端面也提出了一定的要求。规定:螺栓孔按IT8级公差等级和表面粗糙度Ra应不大于6.3μm加工;两螺栓孔在大头孔剖分面的对称度公差为0.25 mm。
5 结合面的技术要求
在连杆受动载荷时,接合面的歪斜使连杆盖及连杆体沿着剖分面产生相对错位,影响到曲轴的连杆轴颈和轴瓦结合不良,从而产生不均匀磨损。结合面的平行度将影响到连杆体、连杆盖和垫片贴合的紧密程度,因而也影响到螺栓的受力情况和曲轴、轴瓦的磨损。对于本连杆,要求结合面的平面度的公差为0.025 mm。
[来源:http://Doc163.com]
 [资料来源:www.doc163.com]
[资料来源:www.doc163.com] 
目录
第一章 绪 论 7
第二章 连杆的结构分析和技术要求 8
2.1 连杆的结构分析 8
2.2 连杆的技术要求 9
第三章 连杆毛坯类型的选择和工艺路线的制订 10
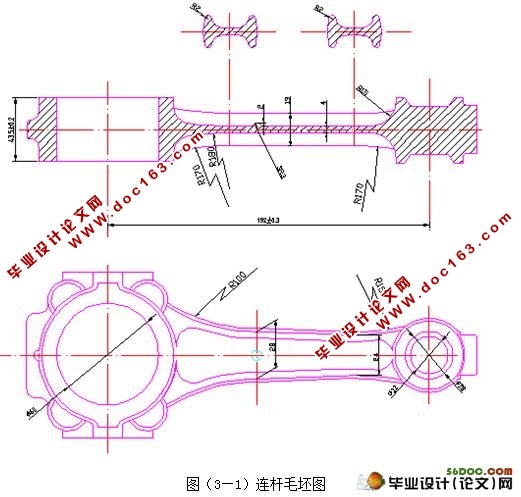
3.1 连杆的材料和毛坯类型的选择 10
3.2 连杆工艺过程的安排 11
3.3 连杆的机械加工工艺过程分析 13
3.3.1 工艺过程的安排 13
3.3.2 定位基准的选择 14
3.3.3 确定合理的夹紧方案 15
3.3.4 各孔及面的加工 16
3.4 确定各工序的加工余量 17
3.4.1 确定大小头两平面加工尺寸 17
3.4.2 确定大头孔加工尺寸 17
3.4.3 小头孔各工序尺寸及其公差 18
3.5 计算50道工序工艺尺寸链 18
3.5.1 连杆盖上轴瓦锁口槽的计算 18
3.5.2 连杆盖上轴瓦锁口槽的计算 19
第四章 对工艺规程部分工序的说明 21
第五章 夹具设计和分析 23
5.1 扩大头孔的方法和要求 23
5.2 定位基准和夹紧方案 23
5.3 夹具的设计 24
5.4 夹具体设计 24
5.5 切削力及夹紧力的计算 26
5.5.1切削力的计算 26
5.5.2夹紧力的计算 27
5.6 夹具精度分析 28
第六章 全文总结 30
参考文献 31
致 谢 32
毕业设计小结 33 [来源:http://www.doc163.com]
下一篇:连杆工艺设计及有限元分析(CAD,Proe三维建模)
