基于AT89C52单片机环境噪声监测电路的设计
基于AT89C52单片机环境噪声监测电路的设计(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文9500字)
摘 要
社会的进步,时代的变迁带来的不止是科技的进步,还有更加不可忽视的环境污染。环境污染不仅包括传统的水污染、空气污染、土壤污染,还包括最近几年日益加剧的噪声污染。
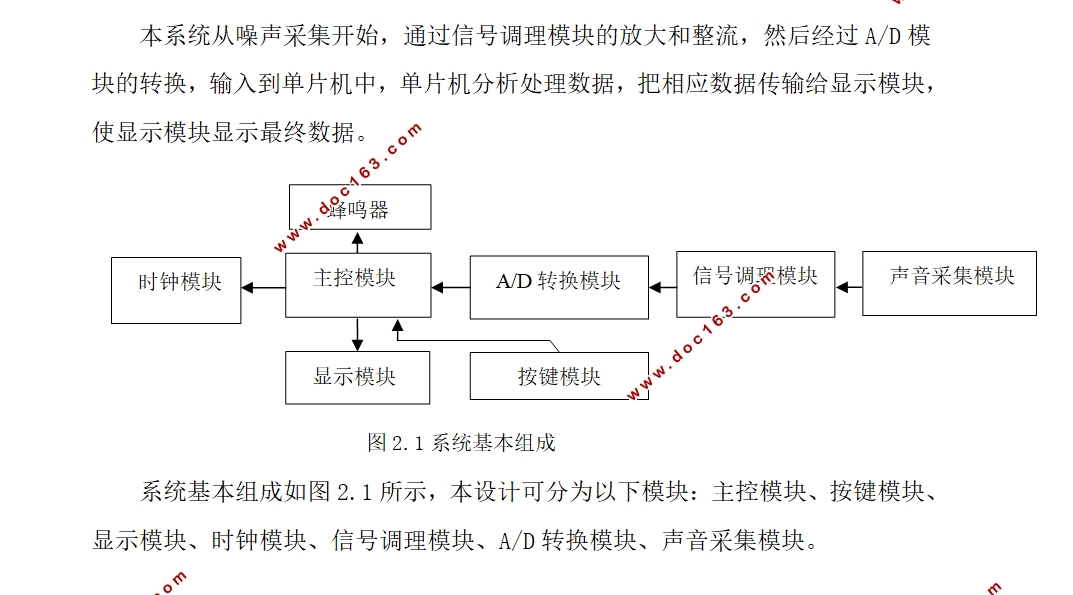
环境噪声监测电路采用了AT89C52单片机为核心,由传声器将声音转换为电信号后,通过由全波整流电路把交流信号转变成直流,再通过低通滤波器变成有效值滤除波动。然后将放大后的信号送入由TLC549组成的模数转换电路转变成数字量。最后通过单片机控制LCD1602把实时的噪声分贝值显示。除此之外系统还带有时钟日历显示和闹钟提醒的功能,用户可以通过按键调节各种事件参数。
关键词:噪声污染 AT89C52 整流电路 LCD1602
The design of environmental noise monitoring circuit
ABSTRACT
Social progress is not just technological advances brought about by the change of the times, there is more pollution that cannot be ignored. Environmental pollution not only include traditional water pollution, air pollution, soil contamination, including increasing noise pollution in recent years. [来源:http://Doc163.com]
Environmental noise monitoring circuit AT89C52 MCU core, when Microphones convert sound to electrical signals, using full-wave rectifier circuit turn AC into DC, then filter through the low-pass filter into a valid value fluctuations. Then into the amplified signal consists of TLC549 of a/d conversion circuit converted to digital. Final adoption of the single-chip computer control of LCD1602 noise DB value display in real time. In addition system with a clock calendar display and alarm reminder features, users can adjust by pressing the event parameters.
Keywords: Noise pollution;AT89C52; Rectifier circuit;LCD1602
[版权所有:http://DOC163.com]


目 录
第一章 引言 1
1.1 目的和意义 1
1.2 现状与发展 1
1.3方案选择 2
1.4本论文的设计任务 2
第二章 环境噪声监测电路的硬件设计 3
2.1 系统设计硬件要求 3 [资料来源:http://Doc163.com]
2.2 总体方案论证与设计 3
2.3主控模块的设计 3
2.3.2 单片机最小系统 4
2.4 显示模块的设计 4
2.4.1 显示器的选择 5
2.4.2 显示模块与单片机模块的连接 5
2.5 按键模块的设计 5
2.6蜂鸣器模块的设计 6
2.7时钟模块的设计 6
2.7.1 时钟模块芯片的选择 6
2.7.2 DS1302的特性: 7
2.7.3 时钟和日历的设计 7
2.7.4 DS1302时钟电路设计 8
2.8 声音采集模块的设计 8
2.8.1 传声器的选择 8
2.8.2信号调理模块的设计 9
2.9 A/D转换模块的设计 10
2.10 本章小结 10
第三章 系统软件设计 11
3.1 程序设计的语言选择 11
3.2 程序设计遵循的原则 11
3.3 程序模块化设计 12
3.3.1 主程序设计 12
3.3.2 系统时钟模块程序设计 12
3.3.3 系统显示程序的设计 13
3.3.4 系统AD转换模块程序的设计 14
3.3.5 系统按键程序的设计 15
3.4 本章总结 17
第四章 系统调试及结果 18
4.1硬件调试 18
4.2软件调试 18
4.3调试结果 18
4.4运行结果 18
4.5 本章小结 20
第五章 结论 21
参考文献 22
致谢 24
附录 25
